- What is Ethereum (ETH)?
- What is Ethereum(ETH) 2.0?
- Ethereum (ETH) 2.0: Why We Need It
- Ethereum (ETH) 2.0 and Ethereum’s Istanbul
- Ethereum (ETH) Network Forks
- Ethereum (ETH) 2.0 Launch Date
- Ethereum (ETH) 2.0 Roadmap
- Ethereum (ETH) 2.0 Price
- Mining on Ethereum (ETH) 2.0
- Decentralized Applications (dApps) on Ethereum (ETH) 2.0
- Pros and Cons of Ethereum (ETH) 2.0
- Experts About Ethereum 2.0 (ETH)
- Ethereum (ETH) 2.0: Summary in Five Points
Ethereum’s Istanbul Hard Fork, which was recently launched, is not only important in itself. This hard fork is probably the last upgrade of such level before the Ethereum 2.0 migration.
It will be Ethereum without mining.
It will be Ethereum consisting of interconnected parts or shards.
It will be Ethereum with staking.
In short, no network has ever conducted such a migration. Therefore, nobody knows precisely how it will function. U.Today has compiled all of the information to let its readers judge whether Ethereum 2.0 is a good idea.
What is Ethereum (ETH)?
Ethereum (Ethereum Network, Ether, ETH) is a blockchain that acts as a host for decentralized applications or decentralized computing service. Ethereum operations are executed via the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Ether is the cryptocurrency generated by the Ethereum platform and used to compensate mining nodes for computations performed. Each account on the Ethereum network has its own address and balance.
Ethereum was proposed in late 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, a cryptocurrency researcher and programmer. Development of this blockchain was funded by an online crowdsale between July and August 2014. The system went live on July 30, 2015. This accounts for about 68 % of the total circulating supply in 2019.
What is Ethereum(ETH) 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0, which has also been dubbed ETH2 or Serenity, is Ethereum's major network upgrade. It will bring several new features to the Ethereum network including the following:
-
Sharding,
-
Proof-of-Stake consensus,
-
A new virtual machine (mechanism that executes network scripts) called Ethereum WebAssembly (eWASM),
-
Scalability and dApp building solutions,
-
New rewards mechanism
-
and more.
Ethereum 2.0 is not backwards compatible, putting an end Ethereum’s old Proof-of-Work (PoW), mining, and full blockchain validation of transactions.
This shall result in a completely new network with redesigned economics, consensus, and mechanism of operation.
Ethereum (ETH) 2.0: Why We Need It

Like any systemwide upgrade, Ethereum 2.0 pursues ambitious targets. In accordance to Danny Ryan, core developer of the Ethereum Foundation, there are five goals for Ethereum 2.0:
-
Simplicity. The complexity of the network should be minimized at the cost of some losses in efficiency.
-
Failure-resistance. The blockchain should be online during major network partitions and when large portions of nodes go offline.
-
Compatibility with quantum hardware. All network elements should either be quantum secure or can easily be swapped out for quantum secure counterparts when available.
-
Decentralization. Maximum participation of validators in total and per unit time should be allowed.
-
Low Entry Price. All processes, including whole system validation, should be available on the average consumer’s laptop.
Ethereum (ETH) 2.0 and Ethereum’s Istanbul
As it has already been said, Ethereum’s Istanbul Hard Fork, which was launched on December 8, 2019, didn’t start the Ethereum 2.0 epoch. Instead, the Istanbul Hard Fork opened the door to transition. This includes systemwide upgrades - scalability, speed, low cost of transactions, and cross-chain interoperability. All will be inevitably available in Ethereum 2.0. Even though Ethereum’s Istanbul is not Ethereum 2.0, there wouldn’t be an Ethereum 2.0 without Ethereum’s Istanbul.
Ethereum (ETH) Network Forks
In cryptocurrencies, a fork usually means a radical change in the way a blockchain validates transactions. There are two types of forks. A hard fork is a change in which old-ruled software will see blocks produced in accordance to new rules as invalid. A soft fork is a fork in the blockchain in which old network nodes and newly upgraded nodes follow different rules. In the case of a hard fork, all nodes are required to work in accordance with the new rules. Therefore, the software needs to be upgraded.
Ethereum (ETH) Early Forks
Most of the known forks for the first years of Ethereum’s existence include Frontier (or Genesis Block, the initial block of Ethereum), which occurred on July 30, 2015, the DAO Fork (resulting from a serious bug in the code that led to a split between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic), and the Byzantium Fork of 2017 (seriously addressed scalability issues).
Some forks have also occurred in emergency situations, including the EIP-150 Hard Fork and the Spurious Dragon Hard Fork.
Ethereum (ETH) 2019 Forks
In 2019, three forks occurred. Two new coins emerged as a result of Ethereum’s Classic Vision Fork (January 11, 2019) and Ethereum’s Nova (January 12, 2019). These forks improved both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic Blockchain.
Ethereum’s Constantinople was the most important fork of Q1-Q2 2019. It started as a Proof of Stake (PoS) transition (a.k.a. Casper update) to make Ethereum faster, cheaper, and more efficient. While no new coins were launched from this upgrade, it did improve the existing protocol.
Ethereum (ETH) 2.0 Launch Date
It’s not so easy to figure out the exact launch date of the network migration onto Ethereum 2.0. In July 2019, it was proclaimed that this process will be launched on January 3, 2020, but this date remains unconfirmed. At the moment, the test environment for the initial stage of Ethereum 2.0 is being prepared by Saphir Labs. So, anyone who uses Parity Ethereum can now enjoy the full end-to-end testnet.
To avoid spreading any fear, uncertainty, or doubt (FUD), the Ethereum Foundation has never disclosed the launch date of Ethereum 2.0. Danny Ryan described the current status of development this way:
“It has never been our launch date. That’s what I’ve been trying to communicate ever since, that date kind of has become pervasive. But we’re all targeting a Q1 launch.”
Thus, we should prepare ourselves for something great in Q1 2020.
Ethereum (ETH) 2.0 Roadmap
The transition to the new network can’t be executed in a flash. Therefore, developers foresee three main phases of Ethereum 1.0’s evolution to Ethereum 2.0:
Phase 0 - Beacon Chain
This is the cornerstone of ETH 2.0, where the PoS consensus will be rolled up. It means that validators (node holders) would need to be registered, rewards and penalties for them would need to be set, and the rules for interaction between them would need to be established. A new Ether (coin) will also emerge during this phase. It is still unclear how it will be issued, but most likely, a special smart contract will allow for a 1:1 exchange of existing ETH.
Phase 1 - Sharding
This is the main load of the new consensus. Shards are the interconnected parts of blockchain (mini-blockchains). With shards, parallel transactions can take place without having the throughput for every transaction within a shard updated on the main chain. As far as the Beacon main chain is concerned, each shard chain block represents a group of data bits. For some time, the current Ethereum (ETH1) and the Ethereum with sharding (ETH2) will co-exist.
Phase 2 - State Execution
During Phase 2, the foundational aspects of the previous ETH 2.0 releases will come together and provide functionality for the updated network. A new operational mechanism called Ethereum WebAssembly (eWASM) will be launched instead of Ethereum’s Virtual Machine. eWASM will work much faster.
Ethereum (ETH) 2.0 Price
It’s really difficult to predict how the transition to Ethereum 2.0 will affect the price of Ethereum. It looks like there are two possible scenarios. If the transition is smooth, then users will be incentivized to participate in the staking process and to buy Ethers. As a result, the demand will grow, and so will the price. The other scenario is that the miners will shut down their equipment, the network will operate slowly, and the users will eventually abandon it.
Those interested in Ethereum 2.0’s price should trace two processes - how the Ethereum Foundation delivers new releases of ETH 2.0 functions, and how these functions work.
Mining on Ethereum (ETH) 2.0
Mining in Ethereum 2.0 will be replaced by staking. Rather than pay miners to secure the network, participants in the network will be paying validators to secure the network. It's vitally important to get the economics of staking right so that the network stays healthy and secure.
If the incentive to stake is too low, then the network will not have the minimum amount of validators necessary to keep the many shards going. If the incentive is too high, then the network is overpaying for security and inflating the price at a rate that is detrimental to the economics of the whole network.
As of today, the minimum stake to become a validator is 32 ETH, or $4,714. This sum needs to be sent to a special contract in order to let the system recognize you as a validator. How much every validator earns depends on how many Ethers will be sent to the contract (i.e. ‘staked’).
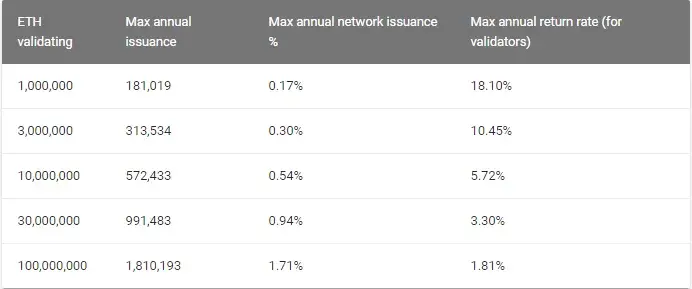
Vitalik Buterin and Justin Drake of the Ethereum Foundation suggest that the most likely number is 5% APR.
Are you interested in becoming an eth2 validator? Check out the first post on staking from #ethereum researcher @carlbeek!https://t.co/En5N4q5WxT?from=article-links
— Ethereum (@ethereum) November 27, 2019
Decentralized Applications (dApps) on Ethereum (ETH) 2.0
The Ethereum 2.0 Hard Fork will significantly improve the attractiveness of the Ethereum platform as a host for dApps. Today, there are two main types of dApps on the Ethereum network - Ethereum Decentralized Exchanges and Ethereum Decentralized Games.
Ethereum (ETH) Decentralized Exchanges
Ethereum Decentralized Exchanges are the exchange services that allow users to swap ERC-20 (Ethereum-based tokens) with each other and without a third-party custody. Well-known decentralized exchanges include Radar Relay, IDT Exchange, Erc dEx and DDEX.
Ethereum (ETH) Decentralized Games
Despite the fact that TRON and EOS are considered the top dApps hosts for games, several popular online gambling services are located on the Ethereum. At the moment, a user can play almost 400 Ethereum games, with My CryptoHeroes and CryptoDozers card games being the most in demand.
Built on ethereum. https://t.co/9xR6wX6bnd?from=article-links
— Built on ethereum. (@builtoneth) December 7, 2019
Pros and Cons of Ethereum (ETH) 2.0
The crucial thing that we should know about the pros and cons of Ethereum 2.0 is that nobody has finalized so sophisticated transition. Therefore, many aspects are still unpredictable.
|
PROS |
CONS |
|
Speed: eWASM is much faster than EVM |
Uncertain economics of Ether as nobody can predict the demand for token |
|
Safety: Cutting-edge security tweaks are to be utilized |
Extremely vulnerable process for token transitions between Ethereum 1.0 to Ethereum 2.0 |
|
Scalability: More side-project solutions are available |
Unclear roadmap: investors can’t design their portfolios until launch dates are set more precisely |
|
Much more advanced consensus |
In case of an unsuccessful transition, the image of Ethereum will be destroyed. EOS and TRON will become more powerful decentralized application hosts |
|
Low electrical consumption |
|
|
Better decentralization |
Experts About Ethereum 2.0 (ETH)
Ethereum (ETH) 2.0: Uncertain Status
For regulators, Ethereum 2.0 still appears as an “uncertain asset”. For example, Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) Chairman Heath Tarbert said that the CFTC is still evaluating whether Ether will remain a commodity under the new model. Ethereum developers and proponents believe that the PoS may actually bolster the case that Ether is “sufficiently decentralized” to be considered a commodity in the eyes of U.S. regulators.
Some Ethereum developers also express concern about migrating from Ethereum 1.0 to Ethereum 2.0. Nirbhik Jangid, an Ethereum developer from India, wrote in Telegram:
Eth 2.0 is a series of network upgrades being carried out to the Ethereum network to increase scalability etc. but will take at least 2 years to be completed, probably longer given the scope of the changes and the challenges involved.
Ethereum (ETH) 2.0: Scalability First
The developers of Ethereum are sure that the main upgrade that can be achieved by Ethereum 2.0 is that of scalability. Vitalik Buterin, the Father of Ethereum, explained it in a podcast:
the main thing that Eth 2.0 makes better is obviously scalability. And scalability is important because of the things that it enables, which basically means more of everything. So the applications that we’ve generally seen on the blockchain so far generally have to do with finance and there’s good reasons for that. Because they like existing centralized financial systems are relatively terrible.
Ethereum (ETH) 2.0: Summary in Five Points
-
Ethereum 2.0 is the next stage of the Ethereum network and will consist of interconnected shards and the use of a Proof-of-Stake algorithm.
-
The transition will most likely start in 2020, with Phase 0 in Q1.
-
Ethereum 2.0 will be required to address the challenges of scalability, speed, decentralization, security, and longevity.
-
There will be no mining in Ethereum 2.0. Staking Ethers will be the only way to obtain a passive income.
-
The major disadvantage for Ethereum 2.0 is the community’s uncertainty, details of the transition, and its future design. This shift is extremely risky for the Ethereum Foundation.

Which feature of Ethereum 2.0 upgrade is the most important for you and why? Share your opinion in Twitter!





 Dan Burgin
Dan Burgin Vladislav Sopov
Vladislav Sopov