First for some context Polygon was originally started as a project called Matic by a team of four in India during 2017. The Matic team set out with a goal to fix some of ethereum's scaling problems and to put India on the map in the blockchain world. They wanted to do this by establishing plasma chains and a proof of stake ethereum side chain. They launched through Binnance’s exchange launch pad. In 2021 the project switched from Matic to Polygon. In this move they set out to create a scaling solution that makes it possible to connect these different scaling solutions in an ecosystem environment where they can communicate with each other. They make it easy for new projects and apps to select which scaling solutions they want. At the time of writing this, polygon has a proof of stake chain and the Matic Plasma Chain. The proof of stake chain is an ethereum virtual machine compatible sidechain. Different apps and projects will have different needs. Some want more security, some want higher speed, some want more independence, and some want cheap transaction costs, and polygon allows them to optimize these needs all in one network. They can also adjust these on the polygon network as time goes on. Additionally, if new scaling solutions become available, polygon can implement them and stay with the times. This makes it attractive for a plethora of projects like NFT market places and gaming that may differ in what their platform needs.
A couple of events and aspects have really driven the recent growth of Polygon
Firstly, the ability for developers to customize their scaling and features has captured the use of many dapps. Their website lists a variety of projects with completely different applications and fields. Some of the big names listed include Aave, Decentraland, and Quickswap. $MATIC liquidity mining is available on the Aave Polygon market. Decentraland has a portal where the $MANA tokens can be moved from the Ethereum blockchain to the polygon network for cheaper gas fees. Quickswap uses the plasma scaling solution to provide cheap and fast transactions. There should be a strong positive correlation between the demand for dapps and the demand for Polygon as it allows for all of the speed, low fees, and customization that cannot be found in any other project at the time of writing this.
Ethereum’s high gas fees have always driven its users to explore side chain options like Polygon. Polygon has near zero gas fees and this has drawn small farmers and investors who have been priced out of ethereum. It has also made it an attractive option for minting NFTs. It also gives app developers a way to achieve low fees and high speeds without having to turn to Binance Smart Chain, which has major drawbacks like it's centralization.
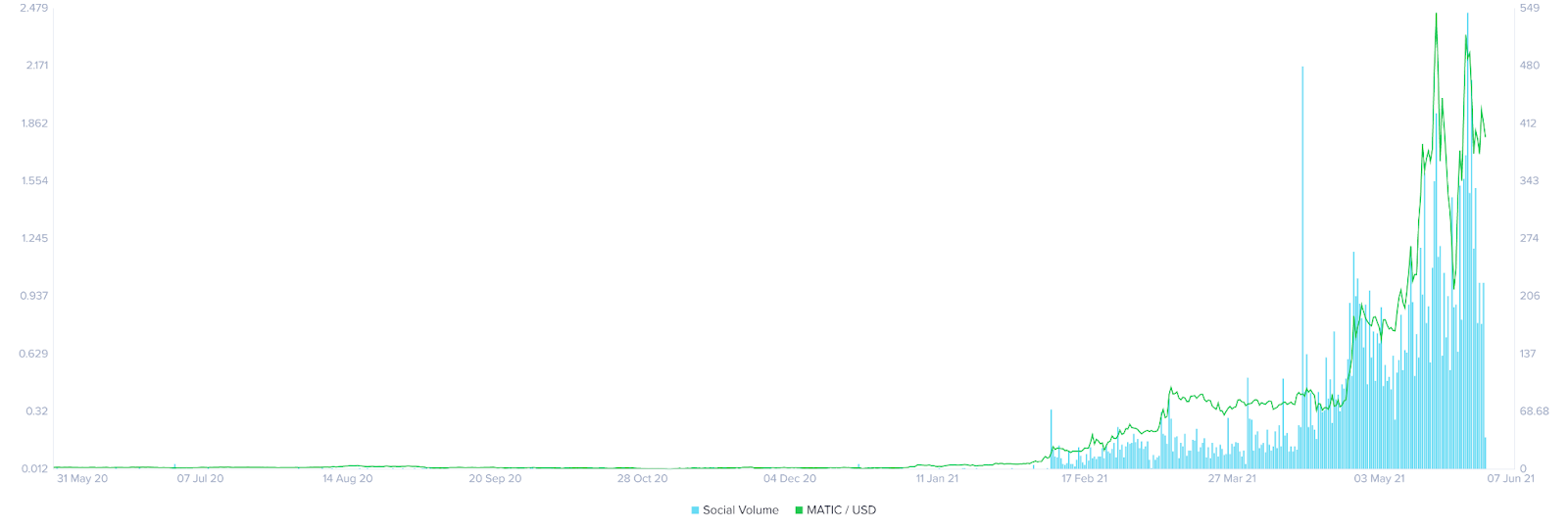
Polygon has almost dominated the social media conversation. This chart depicts the social media volume to its price. It aggregates networks like Twitter, Reddit, Discord, and Telegram. Polygon’s advantages have thrusted it into the conversation which undoubtedly has led to more growth.
It is also available to many casual crypto enthusiasts on the most popular exchanges like CoinBase and Binance. The easy UI and security these exchanges have allows for the masses to invest in Polygon.
Despite popular coins like Bitcoin and Ether taking a hit in the past few weeks, Polygon has almost returned to its all time highs. Big investors like Mark Cuban have also hopped on the train leading to even more popularity. On March 25th he announced he was working to integrate polygon within his NFT website after investing in it. This backing could lead to further institutional investment into the project as he also appears to be working to grow the project.
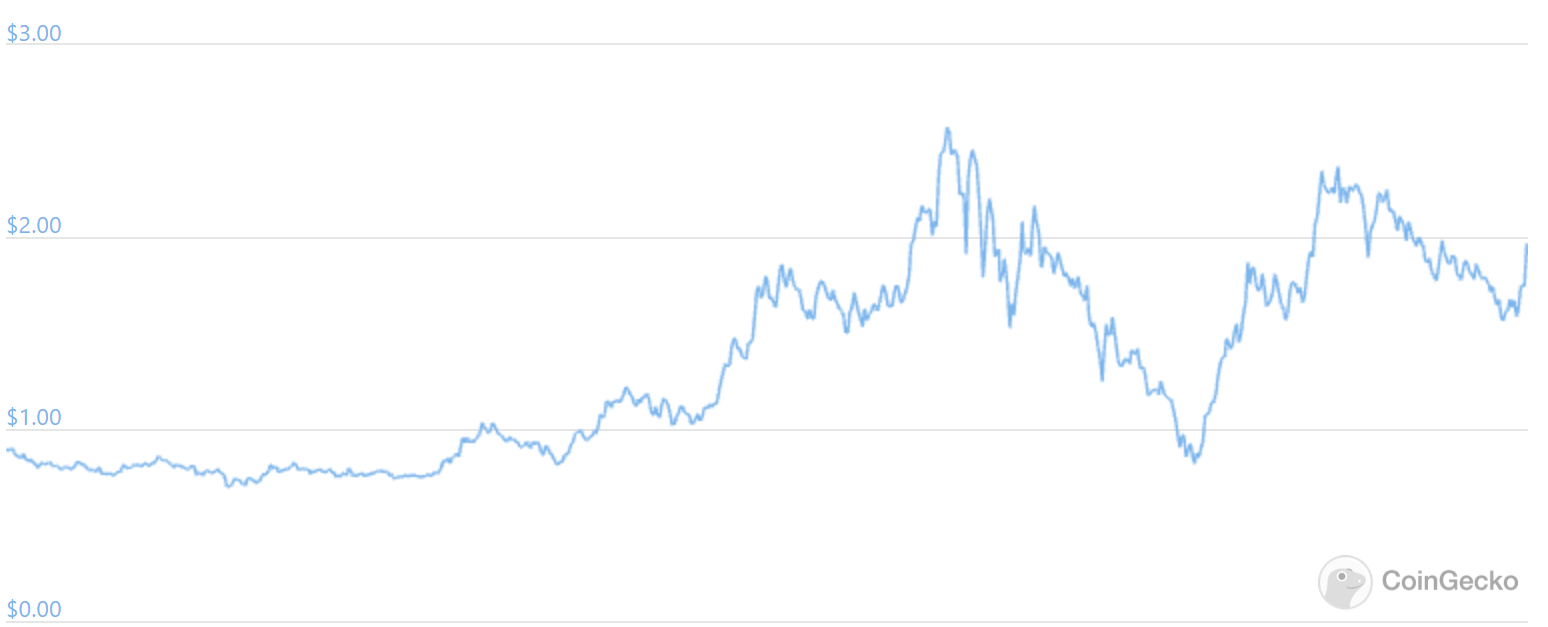
Polygon’s ability to tailor to the needs of developers have allowed it to become a staple of the space. Currently ranked 16th by market capitalization and 17th by trading volume, it does not seem to be going anywhere. Further adoption of crypto and congestion on Ethereum should continue to encourage developers to implement the project. Its rising social media presence and availability on retail exchanges have expanded its reach. Institutions and high net worth individuals like Mark Cuban are just now beginning to hop on the bandwagon which should help continue the project's growth.


 Dan Burgin
Dan Burgin Vladislav Sopov
Vladislav Sopov