- Warning: Undefined array key 1 in Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace::getcard() (line 3178 of modules/custom/cryptocompare/src/TwigExtension/RemoveSpace.php).
Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace::getcard('
Contents
<ul class="article__contents-list"><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h265">Staking Coins: Definition</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h382">Staking Coins: Process</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h424">Top Staking Coins</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h557">Staking Coins: Rewards</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h690">Staking Coins: Five Highlights</a></li></ul>
Advertisement
Every blockchain has its own consensus, ranging from its operating rules to validating transactions. The first blockchains (Bitcoin and Ethereum) utilized a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus, in which every participant’s contribution depended on his/her mining gear.
This scheme requires a lot of electricity and is subject to centralization because of the costs to run and maintain such powerful mining equipment. As a result, the majority of modern blockchains (starting with BitShares) are built around the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus.
With this consensus, an individual needs nothing more from validating coin transactions. It’s from this consensus that the act of staking comes into play.
Staking Coins: Definition
In a nutshell, staking coins refers to the act of locking them up to verify transactions for cryptocurrencies with Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanisms. Stakers can earn rewards for providing such a service.
What is Staking Coins?
To stake your coins means to lock them up (cease all operations including deposits and withdrawals) in order to validate transactions of a particular cryptocurrency. When you're staking your coins, you’re not able to transfer them. Instead, you will receive periodic rewards.
Staking Coins in Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
In Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) blockchains, <a href="https://u.today/eosio-blockchains-daniel-larimer-told-how-he-will-solve-cpu-issues-on-eos-network">you can stake your coins in favor of some large validator</a>. Let's say that you have 10 coins, but the validator (block producer) has some 1-2 million coins. You don’t need to compete with such teams. Instead, you can stake your coins "in favor" of some large entity. In turn, this entity will share part of its huge staking reward with you.
Who Can Stake Coins?
Staking coins is typically available for everyone who have Proof-of-Stake blockchain coins and any sort of cryptocurrency wallet. Holders of Delegated Proof-of-Stake coins like EOS are also welcome. For some coins, a minimum amount of stake is required, but it is usually equivalent to an amount between $10-100 USD.
Staking Coins: Process
In order to stake your coins, you need to choose your staking pool. This will act as a form of custody, which ensures the blockchain governance that your coins are staked. This will also control the process of rewarding.
Staking Coins on Exchanges
Staking coins on an exchange is well-known opportunity for available, even for newbies in crypto. Exchanges usually provide a rich toolkit for deposits, withdrawals, and exchanging coins before staking.
At the moment, 8 exchanges offer the coin staking option with up to 16 available coins. The old exchange moguls KuCoin and Kraken, which are among the top staking platforms with Coinbase, with launch soon. An exchange typically charges fees for their services, which can be between 5-15%.
Staking Coins in Wallets
Numerous staking environments have built-in options within their crypto wallets. This is considered much safer due to the fact that non-exchange wallets are less frequently hacked. The most well-known players include Huobi Wallet, Trust Wallet, and Hashquark. Staking coins in wallets has one important disadvantage - high fees. Wallets can charge you between 25-30% in fees.
Staking Coins with Staking Providers
A staking provider is a special type of crypto service devoted to staking. Many of the staking providers are registered within Europe, which is not common for other types of staking ecosystems. The assortment of coins available for staking is smaller than those available for wallets. The fee rates for staking providers vary between 2% and 50%. So, a staker needs to be extremely cautious.
Top Staking Wallets
Top Staking Exchanges
Top Staking Providers
Binance
Trust Wallet
SNZ Pool
KuCoin
Hash Quark
Staked
Kraken
Huobi Wallet
Bitcoin Suisse AG
Staking Coins on Binance
Binance staking is a well-known staking ecosystem based on Binance, the world's largest centralized crypto exchange. At the moment, Binance provides an individual with the opportunity to stake 14 coins (Tron, Tezos, and Atom are the most popular cryptocurrencies).
Users here can stake for high annual rewards (up to 20% for Algorand tokens), enjoy initial bonuses, and extra rewards sponsored by teams whose tokens are available for staking.
<a href="https://u.today/stellar-staking-terminated-by-binance-as-xlm-inflation-disabled ">card</a>
Top Staking Coins
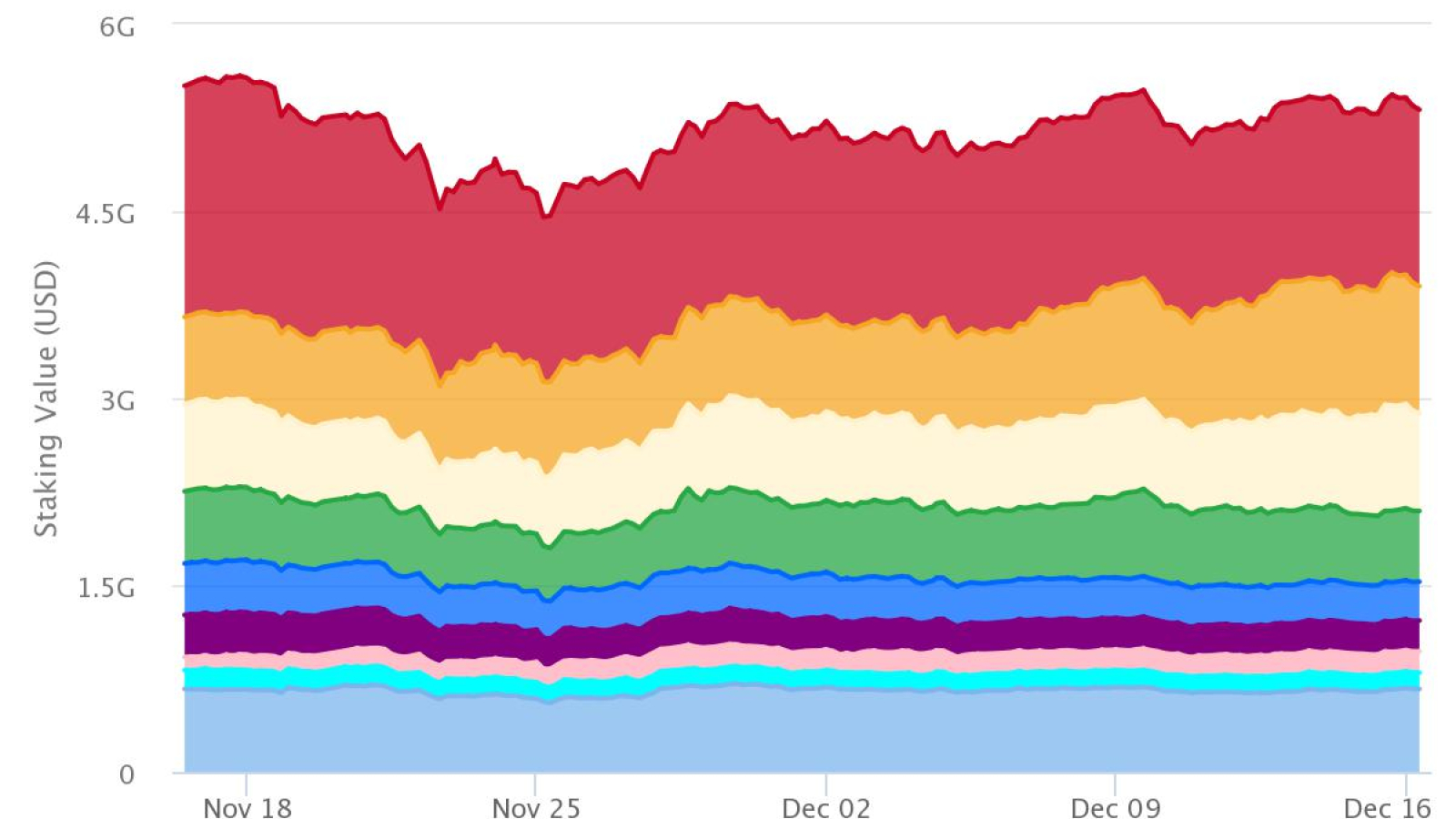
According to StakingRewards.com, 60 different types of crypto assets are currently available for staking through exchanges, wallets, and staking providers. Some of them are well-known and have enormous capitalization (EOS with $2.4 billion or Tezos with $1.1 billion market cap), while others have been evaluated below $100K.
Best Staking Coins of 2019
Throughout 2019, the staking market was extremely conservative with a strong dominance towards the "old" DPoS tokens. The top staking coin was EOS, which is usually staked directly by block producers.
Tezos (XTZ) and Cosmos (ATOM) are among the other two best performers. All coins outside the top list account for only 1.6% of the staking market. From the looks of it, the staking coins sphere in 2019 has been extremely dominated by whales.
<a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="# ">card</a>
Best Staking Coins for 2020
It looks like the situation may remain untouched in 2020. Yet, there are some tokens that could potentially skyrocket in this area.
One potential candidate is the Ethereum 2.0 token. As ETH2 will utilize the Proof-of-Stake consensus, this token will be available for staking. According to ETH2 developers, the expected annual rewards will be between 4 and 5%.
<a href="https://u.today/staking-and-validation-details-in-ethereum-20-disclosed ">card</a>
Other prospective projects set to launch their staking operations include Cardano and Polkadot. Both teams have announced plans to start staking in 2020, with expected rewards to be between 3.5 and 4%.
Staking EOS
Staking is inevitable in EOS because it grants your account resources (memory and capacity) that are required to perform any actions on the blockchain. When you stake bandwidth, you will be allowed to send more transactions within a certain period of time as the size of the transaction consumes the bandwidth.
To use the network, an average user will only need to stake 1 or 2 EOS. However, the amount of EOS staked is also tied to your voting power. Only staked tokens contribute to voting power when an individual votes for Block Producers.
In order to stake your EOS, you need to perform the following steps:
<ol>
<li dir="ltr">
Install <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://github.com/GetScatter/ScatterDesktop/releases/">Scatter</a> or any other application required to browse through the EOS network.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Open the dashboard of your staking provider - block producer or exchange. It will usually look something like this:
</li>
</ol>
<em>Image by: <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://www.eosx.io/guides/how-to-stake-tokens">https://www.eosx.io/guides/how-to-stake-tokens</a> </em>
3. Choose the type of resource you would like to grant to your delegate (block producer) and the amount of EOS to stake.
4. Launch the staking process.
Staking Cardano
The Cardano blockchain provides an individual with a unique opportunity to try the staking option in a test environment. This testnet is designed to test the staking framework within a real-world scenario and allow every ADA holder to earn real rewards by either delegating your stake or running a stake pool.
If you want to delegate your stake, you need to download one of the supported wallet clients from the official <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://staking.cardano.org">testnet page</a>. If you want to run a stake pool, visit the stake pool page for more details about how to get started as a stake pool operator.
Cardano also launched the Daedalus Rewards wallet, which allows its users to stake ADA tokens. Coins that are earned can be spent in competition within the testnet.
<a href="https://u.today/cardano-debuts-daedalus-rewards-wallet-for-staking-ada ">card</a>
Staking Coins: Rewards
The annual reward is the most interesting aspect when it comes staking coins. Here, we can define two types of strategies - conservative and high-risk.
Staking Top Coins: Slowly, But Surely
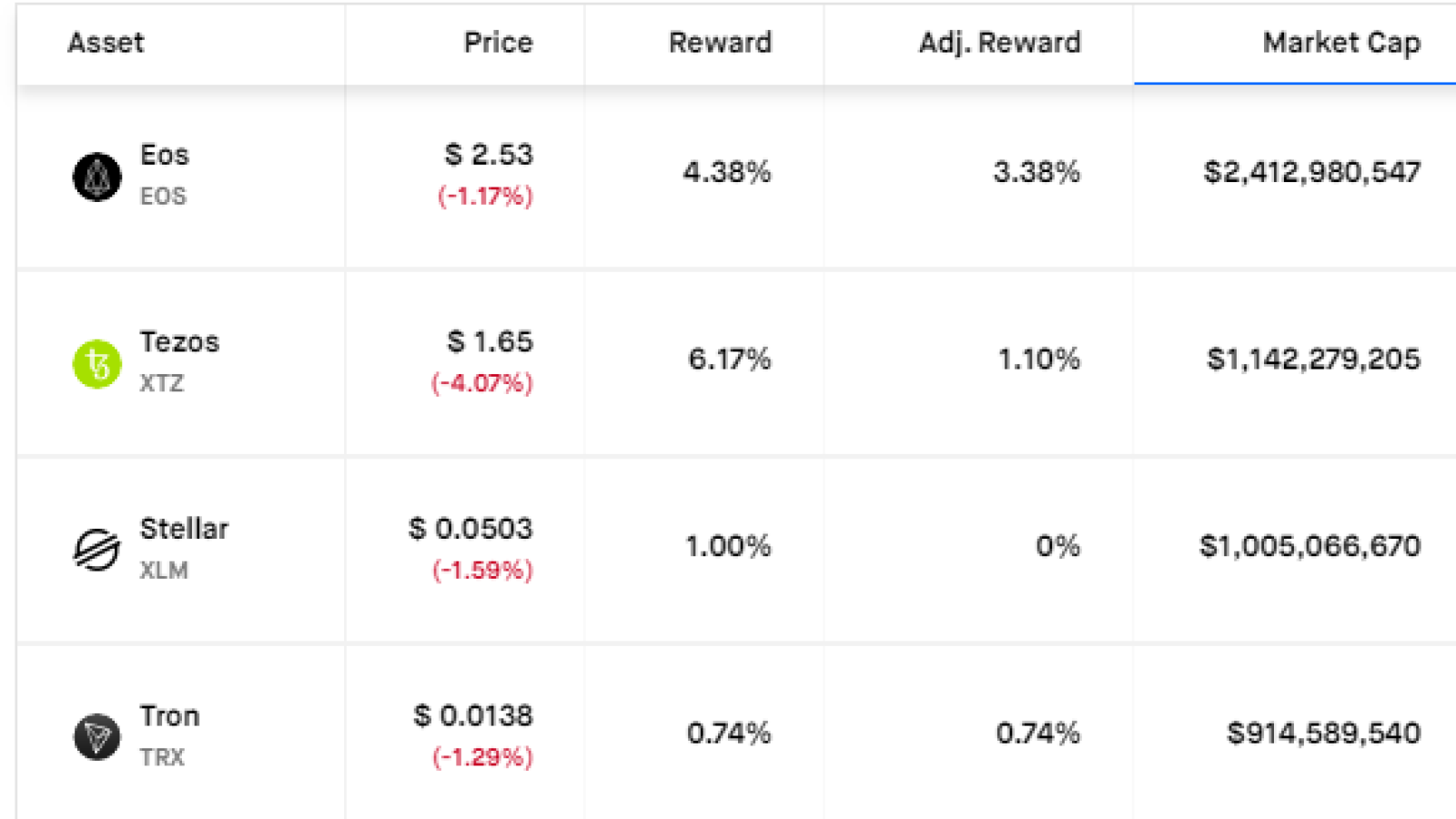
Let’s do the math. The average annual staking reward today is around 10%. Should we take 5 coins with top market capitalization (high demand products, proven progress, etc.), the average earnings will be around 4.15% or less than half of the average.
<em>Image by: <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://www.stakingrewards.com/assets">https://www.stakingrewards.com/assets</a></em>
Thus, if one decides to stake a popular coin, be prepared for low earnings. Furthermore, the volatility of these tokens is more or less predictable, so you can manage your staking portfolio with a better level of confidence.
Staking Underdog Coins: High Yield, High Risk
If we take five assets with low market capitalization, we can see that average annual rate is almost 20%, which is 5 times higher than in the previous example.
These coins are subject to terrific "pump-and-dump" schemes, and all your profits can turn into a pumpkin (recall the recent MATIC case). Therefore, it's much wiser to build a balanced staking portfolio after detailed research on the assets and the teams behind it.
<a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href=" #">card</a>
Staking Coins: Five Highlights
<ol>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins refers to the act of locking them up to help verify transactions.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins is performed to earn some annual rewards.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins can be carried out via exchanges, wallets, or staking providers (pools). All of them charge you with additional service fees.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Top staking coins are EOS, XTZ, and ATOM.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Popular reliable coins are characterized by their low annual earnings, while shady and early-stage projects offer high earnings.
</li>
</ol>
<em>Staking coins image by: https://freepik.com/free-vector/business-infographic-flat-design-with-photo_5171519.htm#page=2&query=infographic&position=1</em>
<em> Are you interested in staking coins? Which asset is the most attractive for you? Tell us in the Comments Section!</em>
') (Line: 1145)
Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace->formatbody(Array) (Line: 54)
__TwigTemplate_75845256f703f5319a38e035b4af7dd9->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 379)
Twig\Template->render(Array, Array) (Line: 40)
Twig\TemplateWrapper->render(Array) (Line: 53)
twig_render_template('themes/cryptod/templates/field--body.html.twig', Array) (Line: 372)
Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeManager->render('field', Array) (Line: 436)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->doRender(Array, ) (Line: 204)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->render(Array) (Line: 474)
Drupal\Core\Template\TwigExtension->escapeFilter(Object, Array, 'html', NULL, 1) (Line: 1002)
__TwigTemplate_625426e732c5f7a66fde6d628d98a6b2->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 62)
__TwigTemplate_e934e56c1e459c359b150360c7169113->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 379)
Twig\Template->render(Array, Array) (Line: 40)
Twig\TemplateWrapper->render(Array) (Line: 53)
twig_render_template('themes/cryptod/templates/node.html.twig', Array) (Line: 372)
Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeManager->render('node', Array) (Line: 436)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->doRender(Array, ) (Line: 204)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->render(Array, ) (Line: 238)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\{closure}() (Line: 583)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->executeInRenderContext(Object, Object) (Line: 239)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->prepare(Array, Object, Object) (Line: 128)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->renderResponse(Array, Object, Object) (Line: 90)
Drupal\Core\EventSubscriber\MainContentViewSubscriber->onViewRenderArray(Object, 'kernel.view', Object)
call_user_func(Array, Object, 'kernel.view', Object) (Line: 111)
Drupal\Component\EventDispatcher\ContainerAwareEventDispatcher->dispatch(Object, 'kernel.view') (Line: 187)
Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel->handleRaw(Object, 1) (Line: 76)
Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 58)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\Session->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 48)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\KernelPreHandle->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 191)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->fetch(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 128)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->lookup(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 82)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 48)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\ReverseProxyMiddleware->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 51)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\NegotiationMiddleware->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 51)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\StackedHttpKernel->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 704)
Drupal\Core\DrupalKernel->handle(Object) (Line: 18)
- Warning: Undefined array key 1 in Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace::getcard() (line 3181 of modules/custom/cryptocompare/src/TwigExtension/RemoveSpace.php).
Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace::getcard('
Contents
<ul class="article__contents-list"><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h265">Staking Coins: Definition</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h382">Staking Coins: Process</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h424">Top Staking Coins</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h557">Staking Coins: Rewards</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h690">Staking Coins: Five Highlights</a></li></ul>
Advertisement
Every blockchain has its own consensus, ranging from its operating rules to validating transactions. The first blockchains (Bitcoin and Ethereum) utilized a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus, in which every participant’s contribution depended on his/her mining gear.
This scheme requires a lot of electricity and is subject to centralization because of the costs to run and maintain such powerful mining equipment. As a result, the majority of modern blockchains (starting with BitShares) are built around the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus.
With this consensus, an individual needs nothing more from validating coin transactions. It’s from this consensus that the act of staking comes into play.
Staking Coins: Definition
In a nutshell, staking coins refers to the act of locking them up to verify transactions for cryptocurrencies with Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanisms. Stakers can earn rewards for providing such a service.
What is Staking Coins?
To stake your coins means to lock them up (cease all operations including deposits and withdrawals) in order to validate transactions of a particular cryptocurrency. When you're staking your coins, you’re not able to transfer them. Instead, you will receive periodic rewards.
Staking Coins in Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
In Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) blockchains, <a href="https://u.today/eosio-blockchains-daniel-larimer-told-how-he-will-solve-cpu-issues-on-eos-network">you can stake your coins in favor of some large validator</a>. Let's say that you have 10 coins, but the validator (block producer) has some 1-2 million coins. You don’t need to compete with such teams. Instead, you can stake your coins "in favor" of some large entity. In turn, this entity will share part of its huge staking reward with you.
Who Can Stake Coins?
Staking coins is typically available for everyone who have Proof-of-Stake blockchain coins and any sort of cryptocurrency wallet. Holders of Delegated Proof-of-Stake coins like EOS are also welcome. For some coins, a minimum amount of stake is required, but it is usually equivalent to an amount between $10-100 USD.
Staking Coins: Process
In order to stake your coins, you need to choose your staking pool. This will act as a form of custody, which ensures the blockchain governance that your coins are staked. This will also control the process of rewarding.
Staking Coins on Exchanges
Staking coins on an exchange is well-known opportunity for available, even for newbies in crypto. Exchanges usually provide a rich toolkit for deposits, withdrawals, and exchanging coins before staking.
At the moment, 8 exchanges offer the coin staking option with up to 16 available coins. The old exchange moguls KuCoin and Kraken, which are among the top staking platforms with Coinbase, with launch soon. An exchange typically charges fees for their services, which can be between 5-15%.
Staking Coins in Wallets
Numerous staking environments have built-in options within their crypto wallets. This is considered much safer due to the fact that non-exchange wallets are less frequently hacked. The most well-known players include Huobi Wallet, Trust Wallet, and Hashquark. Staking coins in wallets has one important disadvantage - high fees. Wallets can charge you between 25-30% in fees.
Staking Coins with Staking Providers
A staking provider is a special type of crypto service devoted to staking. Many of the staking providers are registered within Europe, which is not common for other types of staking ecosystems. The assortment of coins available for staking is smaller than those available for wallets. The fee rates for staking providers vary between 2% and 50%. So, a staker needs to be extremely cautious.
Top Staking Wallets
Top Staking Exchanges
Top Staking Providers
Binance
Trust Wallet
SNZ Pool
KuCoin
Hash Quark
Staked
Kraken
Huobi Wallet
Bitcoin Suisse AG
Staking Coins on Binance
Binance staking is a well-known staking ecosystem based on Binance, the world's largest centralized crypto exchange. At the moment, Binance provides an individual with the opportunity to stake 14 coins (Tron, Tezos, and Atom are the most popular cryptocurrencies).
Users here can stake for high annual rewards (up to 20% for Algorand tokens), enjoy initial bonuses, and extra rewards sponsored by teams whose tokens are available for staking.
<a href="https://u.today/stellar-staking-terminated-by-binance-as-xlm-inflation-disabled ">card</a>
Top Staking Coins
According to StakingRewards.com, 60 different types of crypto assets are currently available for staking through exchanges, wallets, and staking providers. Some of them are well-known and have enormous capitalization (EOS with $2.4 billion or Tezos with $1.1 billion market cap), while others have been evaluated below $100K.
Best Staking Coins of 2019
Throughout 2019, the staking market was extremely conservative with a strong dominance towards the "old" DPoS tokens. The top staking coin was EOS, which is usually staked directly by block producers.
Tezos (XTZ) and Cosmos (ATOM) are among the other two best performers. All coins outside the top list account for only 1.6% of the staking market. From the looks of it, the staking coins sphere in 2019 has been extremely dominated by whales.
<a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="# ">card</a>
Best Staking Coins for 2020
It looks like the situation may remain untouched in 2020. Yet, there are some tokens that could potentially skyrocket in this area.
One potential candidate is the Ethereum 2.0 token. As ETH2 will utilize the Proof-of-Stake consensus, this token will be available for staking. According to ETH2 developers, the expected annual rewards will be between 4 and 5%.
<a href="https://u.today/staking-and-validation-details-in-ethereum-20-disclosed ">card</a>
Other prospective projects set to launch their staking operations include Cardano and Polkadot. Both teams have announced plans to start staking in 2020, with expected rewards to be between 3.5 and 4%.
Staking EOS
Staking is inevitable in EOS because it grants your account resources (memory and capacity) that are required to perform any actions on the blockchain. When you stake bandwidth, you will be allowed to send more transactions within a certain period of time as the size of the transaction consumes the bandwidth.
To use the network, an average user will only need to stake 1 or 2 EOS. However, the amount of EOS staked is also tied to your voting power. Only staked tokens contribute to voting power when an individual votes for Block Producers.
In order to stake your EOS, you need to perform the following steps:
<ol>
<li dir="ltr">
Install <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://github.com/GetScatter/ScatterDesktop/releases/">Scatter</a> or any other application required to browse through the EOS network.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
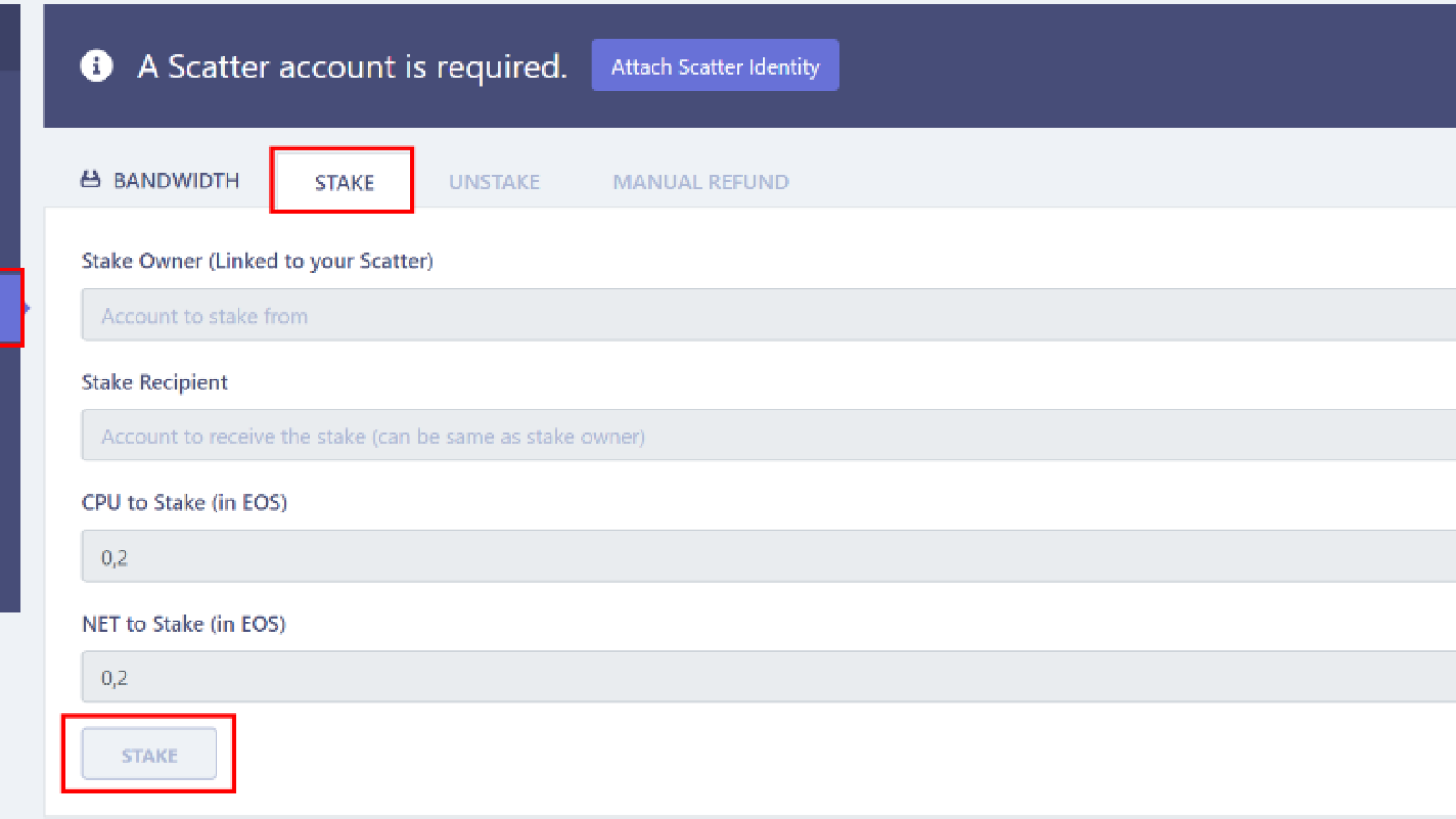
Open the dashboard of your staking provider - block producer or exchange. It will usually look something like this:
</li>
</ol>
<em>Image by: <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://www.eosx.io/guides/how-to-stake-tokens">https://www.eosx.io/guides/how-to-stake-tokens</a> </em>
3. Choose the type of resource you would like to grant to your delegate (block producer) and the amount of EOS to stake.
4. Launch the staking process.
Staking Cardano
The Cardano blockchain provides an individual with a unique opportunity to try the staking option in a test environment. This testnet is designed to test the staking framework within a real-world scenario and allow every ADA holder to earn real rewards by either delegating your stake or running a stake pool.
If you want to delegate your stake, you need to download one of the supported wallet clients from the official <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://staking.cardano.org">testnet page</a>. If you want to run a stake pool, visit the stake pool page for more details about how to get started as a stake pool operator.
Cardano also launched the Daedalus Rewards wallet, which allows its users to stake ADA tokens. Coins that are earned can be spent in competition within the testnet.
<a href="https://u.today/cardano-debuts-daedalus-rewards-wallet-for-staking-ada ">card</a>
Staking Coins: Rewards
The annual reward is the most interesting aspect when it comes staking coins. Here, we can define two types of strategies - conservative and high-risk.
Staking Top Coins: Slowly, But Surely
Let’s do the math. The average annual staking reward today is around 10%. Should we take 5 coins with top market capitalization (high demand products, proven progress, etc.), the average earnings will be around 4.15% or less than half of the average.
<em>Image by: <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://www.stakingrewards.com/assets">https://www.stakingrewards.com/assets</a></em>
Thus, if one decides to stake a popular coin, be prepared for low earnings. Furthermore, the volatility of these tokens is more or less predictable, so you can manage your staking portfolio with a better level of confidence.
Staking Underdog Coins: High Yield, High Risk
If we take five assets with low market capitalization, we can see that average annual rate is almost 20%, which is 5 times higher than in the previous example.
These coins are subject to terrific "pump-and-dump" schemes, and all your profits can turn into a pumpkin (recall the recent MATIC case). Therefore, it's much wiser to build a balanced staking portfolio after detailed research on the assets and the teams behind it.
<a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href=" #">card</a>
Staking Coins: Five Highlights
<ol>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins refers to the act of locking them up to help verify transactions.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins is performed to earn some annual rewards.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins can be carried out via exchanges, wallets, or staking providers (pools). All of them charge you with additional service fees.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Top staking coins are EOS, XTZ, and ATOM.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Popular reliable coins are characterized by their low annual earnings, while shady and early-stage projects offer high earnings.
</li>
</ol>
<em>Staking coins image by: https://freepik.com/free-vector/business-infographic-flat-design-with-photo_5171519.htm#page=2&query=infographic&position=1</em>
<em> Are you interested in staking coins? Which asset is the most attractive for you? Tell us in the Comments Section!</em>
') (Line: 1145)
Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace->formatbody(Array) (Line: 54)
__TwigTemplate_75845256f703f5319a38e035b4af7dd9->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 379)
Twig\Template->render(Array, Array) (Line: 40)
Twig\TemplateWrapper->render(Array) (Line: 53)
twig_render_template('themes/cryptod/templates/field--body.html.twig', Array) (Line: 372)
Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeManager->render('field', Array) (Line: 436)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->doRender(Array, ) (Line: 204)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->render(Array) (Line: 474)
Drupal\Core\Template\TwigExtension->escapeFilter(Object, Array, 'html', NULL, 1) (Line: 1002)
__TwigTemplate_625426e732c5f7a66fde6d628d98a6b2->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 62)
__TwigTemplate_e934e56c1e459c359b150360c7169113->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 379)
Twig\Template->render(Array, Array) (Line: 40)
Twig\TemplateWrapper->render(Array) (Line: 53)
twig_render_template('themes/cryptod/templates/node.html.twig', Array) (Line: 372)
Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeManager->render('node', Array) (Line: 436)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->doRender(Array, ) (Line: 204)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->render(Array, ) (Line: 238)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\{closure}() (Line: 583)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->executeInRenderContext(Object, Object) (Line: 239)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->prepare(Array, Object, Object) (Line: 128)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->renderResponse(Array, Object, Object) (Line: 90)
Drupal\Core\EventSubscriber\MainContentViewSubscriber->onViewRenderArray(Object, 'kernel.view', Object)
call_user_func(Array, Object, 'kernel.view', Object) (Line: 111)
Drupal\Component\EventDispatcher\ContainerAwareEventDispatcher->dispatch(Object, 'kernel.view') (Line: 187)
Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel->handleRaw(Object, 1) (Line: 76)
Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 58)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\Session->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 48)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\KernelPreHandle->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 191)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->fetch(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 128)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->lookup(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 82)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 48)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\ReverseProxyMiddleware->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 51)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\NegotiationMiddleware->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 51)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\StackedHttpKernel->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 704)
Drupal\Core\DrupalKernel->handle(Object) (Line: 18)
- Warning: Undefined array key 1 in Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace::getcard() (line 3178 of modules/custom/cryptocompare/src/TwigExtension/RemoveSpace.php).
Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace::getcard('
Contents
<ul class="article__contents-list"><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h265">Staking Coins: Definition</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h382">Staking Coins: Process</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h424">Top Staking Coins</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h557">Staking Coins: Rewards</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h690">Staking Coins: Five Highlights</a></li></ul>
Advertisement
Every blockchain has its own consensus, ranging from its operating rules to validating transactions. The first blockchains (Bitcoin and Ethereum) utilized a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus, in which every participant’s contribution depended on his/her mining gear.
This scheme requires a lot of electricity and is subject to centralization because of the costs to run and maintain such powerful mining equipment. As a result, the majority of modern blockchains (starting with BitShares) are built around the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus.
With this consensus, an individual needs nothing more from validating coin transactions. It’s from this consensus that the act of staking comes into play.
Staking Coins: Definition
In a nutshell, staking coins refers to the act of locking them up to verify transactions for cryptocurrencies with Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanisms. Stakers can earn rewards for providing such a service.
What is Staking Coins?
To stake your coins means to lock them up (cease all operations including deposits and withdrawals) in order to validate transactions of a particular cryptocurrency. When you're staking your coins, you’re not able to transfer them. Instead, you will receive periodic rewards.
Staking Coins in Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
In Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) blockchains, <a href="https://u.today/eosio-blockchains-daniel-larimer-told-how-he-will-solve-cpu-issues-on-eos-network">you can stake your coins in favor of some large validator</a>. Let's say that you have 10 coins, but the validator (block producer) has some 1-2 million coins. You don’t need to compete with such teams. Instead, you can stake your coins "in favor" of some large entity. In turn, this entity will share part of its huge staking reward with you.
Who Can Stake Coins?
Staking coins is typically available for everyone who have Proof-of-Stake blockchain coins and any sort of cryptocurrency wallet. Holders of Delegated Proof-of-Stake coins like EOS are also welcome. For some coins, a minimum amount of stake is required, but it is usually equivalent to an amount between $10-100 USD.
Staking Coins: Process
In order to stake your coins, you need to choose your staking pool. This will act as a form of custody, which ensures the blockchain governance that your coins are staked. This will also control the process of rewarding.
Staking Coins on Exchanges
Staking coins on an exchange is well-known opportunity for available, even for newbies in crypto. Exchanges usually provide a rich toolkit for deposits, withdrawals, and exchanging coins before staking.
At the moment, 8 exchanges offer the coin staking option with up to 16 available coins. The old exchange moguls KuCoin and Kraken, which are among the top staking platforms with Coinbase, with launch soon. An exchange typically charges fees for their services, which can be between 5-15%.
Staking Coins in Wallets
Numerous staking environments have built-in options within their crypto wallets. This is considered much safer due to the fact that non-exchange wallets are less frequently hacked. The most well-known players include Huobi Wallet, Trust Wallet, and Hashquark. Staking coins in wallets has one important disadvantage - high fees. Wallets can charge you between 25-30% in fees.
Staking Coins with Staking Providers
A staking provider is a special type of crypto service devoted to staking. Many of the staking providers are registered within Europe, which is not common for other types of staking ecosystems. The assortment of coins available for staking is smaller than those available for wallets. The fee rates for staking providers vary between 2% and 50%. So, a staker needs to be extremely cautious.
Top Staking Wallets
Top Staking Exchanges
Top Staking Providers
Binance
Trust Wallet
SNZ Pool
KuCoin
Hash Quark
Staked
Kraken
Huobi Wallet
Bitcoin Suisse AG
Staking Coins on Binance
Binance staking is a well-known staking ecosystem based on Binance, the world's largest centralized crypto exchange. At the moment, Binance provides an individual with the opportunity to stake 14 coins (Tron, Tezos, and Atom are the most popular cryptocurrencies).
Users here can stake for high annual rewards (up to 20% for Algorand tokens), enjoy initial bonuses, and extra rewards sponsored by teams whose tokens are available for staking.
<a href="https://u.today/stellar-staking-terminated-by-binance-as-xlm-inflation-disabled ">card</a>
Top Staking Coins
According to StakingRewards.com, 60 different types of crypto assets are currently available for staking through exchanges, wallets, and staking providers. Some of them are well-known and have enormous capitalization (EOS with $2.4 billion or Tezos with $1.1 billion market cap), while others have been evaluated below $100K.
Best Staking Coins of 2019
Throughout 2019, the staking market was extremely conservative with a strong dominance towards the "old" DPoS tokens. The top staking coin was EOS, which is usually staked directly by block producers.
Tezos (XTZ) and Cosmos (ATOM) are among the other two best performers. All coins outside the top list account for only 1.6% of the staking market. From the looks of it, the staking coins sphere in 2019 has been extremely dominated by whales.
<a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="# ">card</a>
Best Staking Coins for 2020
It looks like the situation may remain untouched in 2020. Yet, there are some tokens that could potentially skyrocket in this area.
One potential candidate is the Ethereum 2.0 token. As ETH2 will utilize the Proof-of-Stake consensus, this token will be available for staking. According to ETH2 developers, the expected annual rewards will be between 4 and 5%.
<a href="https://u.today/staking-and-validation-details-in-ethereum-20-disclosed ">card</a>
Other prospective projects set to launch their staking operations include Cardano and Polkadot. Both teams have announced plans to start staking in 2020, with expected rewards to be between 3.5 and 4%.
Staking EOS
Staking is inevitable in EOS because it grants your account resources (memory and capacity) that are required to perform any actions on the blockchain. When you stake bandwidth, you will be allowed to send more transactions within a certain period of time as the size of the transaction consumes the bandwidth.
To use the network, an average user will only need to stake 1 or 2 EOS. However, the amount of EOS staked is also tied to your voting power. Only staked tokens contribute to voting power when an individual votes for Block Producers.
In order to stake your EOS, you need to perform the following steps:
<ol>
<li dir="ltr">
Install <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://github.com/GetScatter/ScatterDesktop/releases/">Scatter</a> or any other application required to browse through the EOS network.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Open the dashboard of your staking provider - block producer or exchange. It will usually look something like this:
</li>
</ol>
<em>Image by: <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://www.eosx.io/guides/how-to-stake-tokens">https://www.eosx.io/guides/how-to-stake-tokens</a> </em>
3. Choose the type of resource you would like to grant to your delegate (block producer) and the amount of EOS to stake.
4. Launch the staking process.
Staking Cardano
The Cardano blockchain provides an individual with a unique opportunity to try the staking option in a test environment. This testnet is designed to test the staking framework within a real-world scenario and allow every ADA holder to earn real rewards by either delegating your stake or running a stake pool.
If you want to delegate your stake, you need to download one of the supported wallet clients from the official <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://staking.cardano.org">testnet page</a>. If you want to run a stake pool, visit the stake pool page for more details about how to get started as a stake pool operator.
Cardano also launched the Daedalus Rewards wallet, which allows its users to stake ADA tokens. Coins that are earned can be spent in competition within the testnet.
<a href="https://u.today/cardano-debuts-daedalus-rewards-wallet-for-staking-ada ">card</a>
Staking Coins: Rewards
The annual reward is the most interesting aspect when it comes staking coins. Here, we can define two types of strategies - conservative and high-risk.
Staking Top Coins: Slowly, But Surely
Let’s do the math. The average annual staking reward today is around 10%. Should we take 5 coins with top market capitalization (high demand products, proven progress, etc.), the average earnings will be around 4.15% or less than half of the average.
<em>Image by: <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://www.stakingrewards.com/assets">https://www.stakingrewards.com/assets</a></em>
Thus, if one decides to stake a popular coin, be prepared for low earnings. Furthermore, the volatility of these tokens is more or less predictable, so you can manage your staking portfolio with a better level of confidence.
Staking Underdog Coins: High Yield, High Risk
If we take five assets with low market capitalization, we can see that average annual rate is almost 20%, which is 5 times higher than in the previous example.
These coins are subject to terrific "pump-and-dump" schemes, and all your profits can turn into a pumpkin (recall the recent MATIC case). Therefore, it's much wiser to build a balanced staking portfolio after detailed research on the assets and the teams behind it.
<a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href=" #">card</a>
Staking Coins: Five Highlights
<ol>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins refers to the act of locking them up to help verify transactions.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins is performed to earn some annual rewards.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins can be carried out via exchanges, wallets, or staking providers (pools). All of them charge you with additional service fees.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Top staking coins are EOS, XTZ, and ATOM.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Popular reliable coins are characterized by their low annual earnings, while shady and early-stage projects offer high earnings.
</li>
</ol>
<em>Staking coins image by: https://freepik.com/free-vector/business-infographic-flat-design-with-photo_5171519.htm#page=2&query=infographic&position=1</em>
<em> Are you interested in staking coins? Which asset is the most attractive for you? Tell us in the Comments Section!</em>
') (Line: 1145)
Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace->formatbody(Array) (Line: 54)
__TwigTemplate_75845256f703f5319a38e035b4af7dd9->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 379)
Twig\Template->render(Array, Array) (Line: 40)
Twig\TemplateWrapper->render(Array) (Line: 53)
twig_render_template('themes/cryptod/templates/field--body.html.twig', Array) (Line: 372)
Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeManager->render('field', Array) (Line: 436)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->doRender(Array, ) (Line: 204)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->render(Array) (Line: 474)
Drupal\Core\Template\TwigExtension->escapeFilter(Object, Array, 'html', NULL, 1) (Line: 1002)
__TwigTemplate_625426e732c5f7a66fde6d628d98a6b2->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 62)
__TwigTemplate_e934e56c1e459c359b150360c7169113->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 379)
Twig\Template->render(Array, Array) (Line: 40)
Twig\TemplateWrapper->render(Array) (Line: 53)
twig_render_template('themes/cryptod/templates/node.html.twig', Array) (Line: 372)
Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeManager->render('node', Array) (Line: 436)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->doRender(Array, ) (Line: 204)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->render(Array, ) (Line: 238)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\{closure}() (Line: 583)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->executeInRenderContext(Object, Object) (Line: 239)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->prepare(Array, Object, Object) (Line: 128)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->renderResponse(Array, Object, Object) (Line: 90)
Drupal\Core\EventSubscriber\MainContentViewSubscriber->onViewRenderArray(Object, 'kernel.view', Object)
call_user_func(Array, Object, 'kernel.view', Object) (Line: 111)
Drupal\Component\EventDispatcher\ContainerAwareEventDispatcher->dispatch(Object, 'kernel.view') (Line: 187)
Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel->handleRaw(Object, 1) (Line: 76)
Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 58)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\Session->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 48)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\KernelPreHandle->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 191)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->fetch(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 128)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->lookup(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 82)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 48)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\ReverseProxyMiddleware->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 51)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\NegotiationMiddleware->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 51)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\StackedHttpKernel->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 704)
Drupal\Core\DrupalKernel->handle(Object) (Line: 18)
- Warning: Undefined array key 1 in Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace::getcard() (line 3181 of modules/custom/cryptocompare/src/TwigExtension/RemoveSpace.php).
Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace::getcard('
Contents
<ul class="article__contents-list"><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h265">Staking Coins: Definition</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h382">Staking Coins: Process</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h424">Top Staking Coins</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h557">Staking Coins: Rewards</a></li><li class="article__contents-item"><a class="article__contents-link link-pseudo" href="#h690">Staking Coins: Five Highlights</a></li></ul>
Advertisement
Every blockchain has its own consensus, ranging from its operating rules to validating transactions. The first blockchains (Bitcoin and Ethereum) utilized a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus, in which every participant’s contribution depended on his/her mining gear.
This scheme requires a lot of electricity and is subject to centralization because of the costs to run and maintain such powerful mining equipment. As a result, the majority of modern blockchains (starting with BitShares) are built around the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus.
With this consensus, an individual needs nothing more from validating coin transactions. It’s from this consensus that the act of staking comes into play.
Staking Coins: Definition
In a nutshell, staking coins refers to the act of locking them up to verify transactions for cryptocurrencies with Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanisms. Stakers can earn rewards for providing such a service.
What is Staking Coins?
To stake your coins means to lock them up (cease all operations including deposits and withdrawals) in order to validate transactions of a particular cryptocurrency. When you're staking your coins, you’re not able to transfer them. Instead, you will receive periodic rewards.
Staking Coins in Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)
In Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) blockchains, <a href="https://u.today/eosio-blockchains-daniel-larimer-told-how-he-will-solve-cpu-issues-on-eos-network">you can stake your coins in favor of some large validator</a>. Let's say that you have 10 coins, but the validator (block producer) has some 1-2 million coins. You don’t need to compete with such teams. Instead, you can stake your coins "in favor" of some large entity. In turn, this entity will share part of its huge staking reward with you.
Who Can Stake Coins?
Staking coins is typically available for everyone who have Proof-of-Stake blockchain coins and any sort of cryptocurrency wallet. Holders of Delegated Proof-of-Stake coins like EOS are also welcome. For some coins, a minimum amount of stake is required, but it is usually equivalent to an amount between $10-100 USD.
Staking Coins: Process
In order to stake your coins, you need to choose your staking pool. This will act as a form of custody, which ensures the blockchain governance that your coins are staked. This will also control the process of rewarding.
Staking Coins on Exchanges
Staking coins on an exchange is well-known opportunity for available, even for newbies in crypto. Exchanges usually provide a rich toolkit for deposits, withdrawals, and exchanging coins before staking.
At the moment, 8 exchanges offer the coin staking option with up to 16 available coins. The old exchange moguls KuCoin and Kraken, which are among the top staking platforms with Coinbase, with launch soon. An exchange typically charges fees for their services, which can be between 5-15%.
Staking Coins in Wallets
Numerous staking environments have built-in options within their crypto wallets. This is considered much safer due to the fact that non-exchange wallets are less frequently hacked. The most well-known players include Huobi Wallet, Trust Wallet, and Hashquark. Staking coins in wallets has one important disadvantage - high fees. Wallets can charge you between 25-30% in fees.
Staking Coins with Staking Providers
A staking provider is a special type of crypto service devoted to staking. Many of the staking providers are registered within Europe, which is not common for other types of staking ecosystems. The assortment of coins available for staking is smaller than those available for wallets. The fee rates for staking providers vary between 2% and 50%. So, a staker needs to be extremely cautious.
Top Staking Wallets
Top Staking Exchanges
Top Staking Providers
Binance
Trust Wallet
SNZ Pool
KuCoin
Hash Quark
Staked
Kraken
Huobi Wallet
Bitcoin Suisse AG
Staking Coins on Binance
Binance staking is a well-known staking ecosystem based on Binance, the world's largest centralized crypto exchange. At the moment, Binance provides an individual with the opportunity to stake 14 coins (Tron, Tezos, and Atom are the most popular cryptocurrencies).
Users here can stake for high annual rewards (up to 20% for Algorand tokens), enjoy initial bonuses, and extra rewards sponsored by teams whose tokens are available for staking.
<a href="https://u.today/stellar-staking-terminated-by-binance-as-xlm-inflation-disabled ">card</a>
Top Staking Coins
According to StakingRewards.com, 60 different types of crypto assets are currently available for staking through exchanges, wallets, and staking providers. Some of them are well-known and have enormous capitalization (EOS with $2.4 billion or Tezos with $1.1 billion market cap), while others have been evaluated below $100K.
Best Staking Coins of 2019
Throughout 2019, the staking market was extremely conservative with a strong dominance towards the "old" DPoS tokens. The top staking coin was EOS, which is usually staked directly by block producers.
Tezos (XTZ) and Cosmos (ATOM) are among the other two best performers. All coins outside the top list account for only 1.6% of the staking market. From the looks of it, the staking coins sphere in 2019 has been extremely dominated by whales.
<a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="# ">card</a>
Best Staking Coins for 2020
It looks like the situation may remain untouched in 2020. Yet, there are some tokens that could potentially skyrocket in this area.
One potential candidate is the Ethereum 2.0 token. As ETH2 will utilize the Proof-of-Stake consensus, this token will be available for staking. According to ETH2 developers, the expected annual rewards will be between 4 and 5%.
<a href="https://u.today/staking-and-validation-details-in-ethereum-20-disclosed ">card</a>
Other prospective projects set to launch their staking operations include Cardano and Polkadot. Both teams have announced plans to start staking in 2020, with expected rewards to be between 3.5 and 4%.
Staking EOS
Staking is inevitable in EOS because it grants your account resources (memory and capacity) that are required to perform any actions on the blockchain. When you stake bandwidth, you will be allowed to send more transactions within a certain period of time as the size of the transaction consumes the bandwidth.
To use the network, an average user will only need to stake 1 or 2 EOS. However, the amount of EOS staked is also tied to your voting power. Only staked tokens contribute to voting power when an individual votes for Block Producers.
In order to stake your EOS, you need to perform the following steps:
<ol>
<li dir="ltr">
Install <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://github.com/GetScatter/ScatterDesktop/releases/">Scatter</a> or any other application required to browse through the EOS network.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Open the dashboard of your staking provider - block producer or exchange. It will usually look something like this:
</li>
</ol>
<em>Image by: <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://www.eosx.io/guides/how-to-stake-tokens">https://www.eosx.io/guides/how-to-stake-tokens</a> </em>
3. Choose the type of resource you would like to grant to your delegate (block producer) and the amount of EOS to stake.
4. Launch the staking process.
Staking Cardano
The Cardano blockchain provides an individual with a unique opportunity to try the staking option in a test environment. This testnet is designed to test the staking framework within a real-world scenario and allow every ADA holder to earn real rewards by either delegating your stake or running a stake pool.
If you want to delegate your stake, you need to download one of the supported wallet clients from the official <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://staking.cardano.org">testnet page</a>. If you want to run a stake pool, visit the stake pool page for more details about how to get started as a stake pool operator.
Cardano also launched the Daedalus Rewards wallet, which allows its users to stake ADA tokens. Coins that are earned can be spent in competition within the testnet.
<a href="https://u.today/cardano-debuts-daedalus-rewards-wallet-for-staking-ada ">card</a>
Staking Coins: Rewards
The annual reward is the most interesting aspect when it comes staking coins. Here, we can define two types of strategies - conservative and high-risk.
Staking Top Coins: Slowly, But Surely
Let’s do the math. The average annual staking reward today is around 10%. Should we take 5 coins with top market capitalization (high demand products, proven progress, etc.), the average earnings will be around 4.15% or less than half of the average.
<em>Image by: <a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href="https://www.stakingrewards.com/assets">https://www.stakingrewards.com/assets</a></em>
Thus, if one decides to stake a popular coin, be prepared for low earnings. Furthermore, the volatility of these tokens is more or less predictable, so you can manage your staking portfolio with a better level of confidence.
Staking Underdog Coins: High Yield, High Risk
If we take five assets with low market capitalization, we can see that average annual rate is almost 20%, which is 5 times higher than in the previous example.
These coins are subject to terrific "pump-and-dump" schemes, and all your profits can turn into a pumpkin (recall the recent MATIC case). Therefore, it's much wiser to build a balanced staking portfolio after detailed research on the assets and the teams behind it.
<a rel="nofollow" target="_blank" href=" #">card</a>
Staking Coins: Five Highlights
<ol>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins refers to the act of locking them up to help verify transactions.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins is performed to earn some annual rewards.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Staking coins can be carried out via exchanges, wallets, or staking providers (pools). All of them charge you with additional service fees.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Top staking coins are EOS, XTZ, and ATOM.
</li>
<li dir="ltr">
Popular reliable coins are characterized by their low annual earnings, while shady and early-stage projects offer high earnings.
</li>
</ol>
<em>Staking coins image by: https://freepik.com/free-vector/business-infographic-flat-design-with-photo_5171519.htm#page=2&query=infographic&position=1</em>
<em> Are you interested in staking coins? Which asset is the most attractive for you? Tell us in the Comments Section!</em>
') (Line: 1145)
Drupal\cryptocompare\TwigExtension\RemoveSpace->formatbody(Array) (Line: 54)
__TwigTemplate_75845256f703f5319a38e035b4af7dd9->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 379)
Twig\Template->render(Array, Array) (Line: 40)
Twig\TemplateWrapper->render(Array) (Line: 53)
twig_render_template('themes/cryptod/templates/field--body.html.twig', Array) (Line: 372)
Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeManager->render('field', Array) (Line: 436)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->doRender(Array, ) (Line: 204)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->render(Array) (Line: 474)
Drupal\Core\Template\TwigExtension->escapeFilter(Object, Array, 'html', NULL, 1) (Line: 1002)
__TwigTemplate_625426e732c5f7a66fde6d628d98a6b2->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 62)
__TwigTemplate_e934e56c1e459c359b150360c7169113->doDisplay(Array, Array) (Line: 394)
Twig\Template->displayWithErrorHandling(Array, Array) (Line: 367)
Twig\Template->display(Array) (Line: 379)
Twig\Template->render(Array, Array) (Line: 40)
Twig\TemplateWrapper->render(Array) (Line: 53)
twig_render_template('themes/cryptod/templates/node.html.twig', Array) (Line: 372)
Drupal\Core\Theme\ThemeManager->render('node', Array) (Line: 436)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->doRender(Array, ) (Line: 204)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->render(Array, ) (Line: 238)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\{closure}() (Line: 583)
Drupal\Core\Render\Renderer->executeInRenderContext(Object, Object) (Line: 239)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->prepare(Array, Object, Object) (Line: 128)
Drupal\Core\Render\MainContent\HtmlRenderer->renderResponse(Array, Object, Object) (Line: 90)
Drupal\Core\EventSubscriber\MainContentViewSubscriber->onViewRenderArray(Object, 'kernel.view', Object)
call_user_func(Array, Object, 'kernel.view', Object) (Line: 111)
Drupal\Component\EventDispatcher\ContainerAwareEventDispatcher->dispatch(Object, 'kernel.view') (Line: 187)
Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel->handleRaw(Object, 1) (Line: 76)
Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 58)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\Session->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 48)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\KernelPreHandle->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 191)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->fetch(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 128)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->lookup(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 82)
Drupal\page_cache\StackMiddleware\PageCache->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 48)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\ReverseProxyMiddleware->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 51)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\NegotiationMiddleware->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 51)
Drupal\Core\StackMiddleware\StackedHttpKernel->handle(Object, 1, 1) (Line: 704)
Drupal\Core\DrupalKernel->handle(Object) (Line: 18)